Bootstrapping a Github Organization
Steps
Create a bot user on Github.
Create an Organization on Github.
Go to Settings -> Member Privileges -> Set the Following Properties
Set Base permission as Read
Disable Private & Public Repository Creation
Disable
Allow members to change repository visibilities for this organization&Allow members to delete or transfer repositories for this organization.
The above settings will disable repository creation for the organization members and disable members with admin privileges to change repository visibility or ability to transfer repositories.
Create a Repository
<organization-name>-github-configwhich will have all the github infrastructure(Repos & User files) for your organization and the tfstate.Setup Branch protection for your Repository so no one can commit into master directly rather create a PR and then have it approved and then merge it onto master.
Go to Repo -> Settings -> Branches -> Branch Protection Rule -> Add Rule. Set following values
Branch Name Pattern: master
Enable
Require pull request reviews before merging, Set the number of approvers required, 1 is default and is enough.You can also enable
Require status checks to pass before merging, so that whenever your PR is created, it should be approved by someone and also its pipeline(CI step) should pass, only then it can merge onto master. We will be creating CI/CD using Github Actions below, you can have your own status checks as well.These are some basic steps that we follow, you can add even more checks based on your organization criteria like signed commits, either this should be for administators as well or not.
Your branch protection page should look like following:
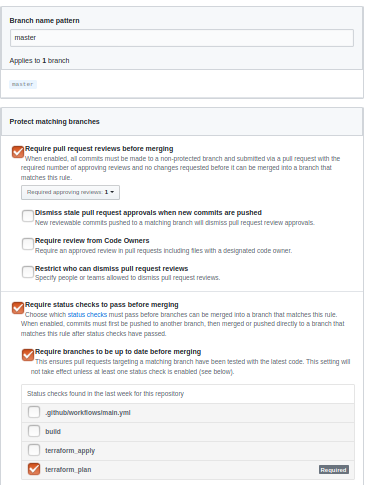
- Add following files with their respective content in the repo.
.gitignore:
File to ignore the files in git
# Compiled files
terraform.tfvars
*.backup
.terraform
*.sh
*.zip
main.tf:
File containing the providers for terraform.
locals{
github_organization = "<organization-name>"
}
provider "github" {
organization = "${local.github_organization}"
version = "1.2.1"
}
terraform {
required_version = ">= 0.11.8"
}
These are the steps that are required to setup your organization. Furthermore, you would have to add users, create teams, create repositories and setup CI/CD for your repository. We recommend following ways, but you can have based on your team policy.
Setup CI/CD using Github Actions
There are different tools through which we can setup CI/CD for our repository like Jenkins, CircleCI, Github Actions, etc. We are using Github Actions for now. You can use the following steps to create CI/CD for your terraform project on Github Actions
- Create folder
.githuband subfolderworkflowsand then create 2 yaml filesci.ymlandcd.yml. Your directory will be like
.github/workflows/ci.yml
.github/workflows/cd.yml
.gitignore
README.md
main.tf
We will be using token of the bot user to create repos so login using bot user and create a Personal Access Token, Go to Profile(top right corner) -> Settings -> Developer Settings -> Personal Access Token and Generate New Token with all rights as through this we will be creating or might be deleting users and repositories. Copy the token.
Go to Repo -> Settings -> Secrets -> Add a Secret, Name should be
GITHUB_TERRAFORM_TOKENand value should be the token that you copied in Step 2.In CI, we will just be validating and planning the terraform, just checking if the PR is fine or not so in
ci.yml, add following content:
name: CI
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- master
jobs:
terraform_plan:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: "!contains(github.event.head_commit.message, 'skip ci')"
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: Install Terraform
env:
TERRAFORM_VERSION: "0.11.11"
run: |
tf_version=$TERRAFORM_VERSION
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/"$tf_version"/terraform_"$tf_version"_linux_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_"$tf_version"_linux_amd64.zip
sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/
- name: Verify Terraform version
run: terraform --version
- name: Terraform init
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TERRAFORM_TOKEN }}
run: terraform init -input=false
- name: Terraform validation
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TERRAFORM_TOKEN }}
run: terraform validate
- name: Terraform plan
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TERRAFORM_TOKEN }}
run: terraform plan
The above manifest will use the token to plan and validate your terraform files and if there is an error it will fail the pipeline. This will be run only for PRs to the master branch.
- In CD, we actually apply the terraform files and save its state in tfstate file, so in cd.yml, copy following manifest
name: CD
on:
push:
branches:
- master
jobs:
terraform_apply:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: "!contains(github.event.head_commit.message, 'skip ci')"
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: Install Terraform
env:
TERRAFORM_VERSION: "0.11.11"
run: |
tf_version=$TERRAFORM_VERSION
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/"$tf_version"/terraform_"$tf_version"_linux_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_"$tf_version"_linux_amd64.zip
sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/
- name: Verify Terraform version
run: terraform --version
- name: Terraform init
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TERRAFORM_TOKEN }}
run: terraform init -input=false
- name: Terraform validation
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TERRAFORM_TOKEN }}
run: terraform validate
- name: Terraform apply
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TERRAFORM_TOKEN }}
run: terraform apply -auto-approve -input=false
- name: Commit files
if: always()
run: |
git config --local user.email "startelvan.bot@gmail.com"
git config --local user.name "Startelvan Bot"
git add .
git commit -m "Update tfstate skip ci" || true
- name: Push changes
if: always()
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TERRAFORM_TOKEN }}
This will only run when a change is committed onto master. It will initialize and apply the terraform manifest and push the changes back to git repository. So when terraform is applied and terraform updates the tfstate file it will push back the changes to the repo.
How TOs
Create a team
Add a file team-developers.tf, copy following manifest in it. Following file will create a Developers team, you can have it based on your own needs.
# Github Team for Developers
resource "github_team" "developers" {
name = "Developers"
description = "A cool team of developers"
privacy = "closed"
}
Add a User
One thing to note is module name should contain
Note
underscore (_) and not hyphen (-)
Add a file user-<username>.tf, copy following manifest in it.
module "user_<user_name>" {
source = "github.com/stakater/terraform-module-github.git//modules/user?ref=1.0.3"
username = "<username>"
team_id = "${github_team.developers.id}"
}
Create a Repository
Add a file repo-<repoName>.tf, for repository there are a number of parameters that you might or might not want for your team, you can see the details below.
One thing to note is module name should contain
Note
underscore (_) and not hyphen (-) whereas in repository name and file name you can use hyphen(-)
so when copying following manifest, take note of this.
module "<repo_name>" {
source = "github.com/stakater/terraform-module-github.git//modules/repository?ref=1.0.10"
name = "<repo-name>"
description = "<Your repo description>"
homepage_url = ""
license_template = ""
team_id = "${github_team.developers.id}"
enable_branch_protection = true
protected_branch_name = "master"
enforce_admins = false
status_checks = ["build"] # name of the pipeline triggered check below
require_status_checks = true
has_wiki = false
has_projects = false
dismiss_stale_reviews = true
require_code_owner_reviews = true
archived = false
has_downloads = true
topics = ["stakater", "development", "golang"]
private = true
webhooks = []
}
Details of Above Parameters:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | String | Name of the Repository |
| description | String | Description of the Repository |
| homepage_url | String | Url for your repository or company |
| license_template | String | If want to set a license for the repository |
| team_id | String | Id of team that should have access to the repository |
| enable_branch_protection | Boolean | Whether the repo should master branch protection enabled |
| protected_branch_name | Boolean | The branch that should be protected |
| enforce_admins | Boolean | Enforce branch protection rule on admins or not |
| status_checks | List of String | The status checks required to pass before merging a repo |
| require_status_checks | Boolean | Whether the branch protection should have status checks enabled or not |
| has_wiki | Boolean | Contains Wiki or Not |
| has_projects | Boolean | Consists of Projects or not |
| dismiss_stale_reviews | Boolean | Dismiss stale reviews when new commits are pushed |
| require_code_owner_reviews | Boolean | Code Owner Review Required |
| archived | Boolean | Is the repo archived or not |
| has_downloads | Boolean | Does the repo contain downloads |
| has_projects | Boolean | Consists of Projects or not |
| topics | Array of String | Topics for the Repository |
| private | Boolean | Repo should be private or public |
| webhooks | Array of Object | Webhooks to be added and their secrets |
Sample Webhook Structure:
webhooks = [
{
url = "https://jenkins.delivery.domain.com/github-webhook/",
events = "push,pull_request"
secret = "mySecret"
}
]
Now the repository will be created, you can setup CI/CD in it. If you want to setup CI/CD through Github Actions, you can do the following:
- Clone the repo
- Create folders .github/workflow
- Create a ci.yml, copy following content
name: CI
on:
pull_request:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: "!contains(github.event.head_commit.message, 'skip ci')"
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: List
run: ls
- name: Build
run: echo helloworld
The above will run on PRs for any branch and its name is build, used in the status_checks parameter above.
Creating PR & Pushing changes
Create a new branch and push your changes to it, and then create a PR for it, PR will trigger a CI pipeline, which will run following steps:
terraform init -input=false
terraform validate
terraform plan
If pipeline passes, you can approve the PR from another member and only then you can merge it to the master branch, which will run the CD pipeline which will actually create the user in the organization and make it a member of team. The CD pipeline does the following steps:
terraform init -input=false
terraform validate
terraform apply -auto-approve -input=false
Push the changes